Source code for random phase noise texture synthesis. The front end functions for texture synthesis are rpn_color_different_size and rpn_color_same_size. More...
#include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>#include <math.h>#include <fftw3.h>#include "mt.h"
Go to the source code of this file.
Defines | |
| #define | M_PI 3.14159265358979323846 |
Functions | |
| static float | mean (float *data_in, size_t N) |
| Compute the mean of a 2D array of float type. | |
| static fftwf_complex * | pointwise_complexfloat_multiplication (fftwf_complex *comp_in, float *float_in, size_t N) |
| Pointwise multiplication of a complex array by a float array. The complex input is modified. | |
| static fftwf_complex * | pointwise_complex_multiplication (fftwf_complex *comp_in1, fftwf_complex *comp_in2, size_t N) |
| Pointwise multiplication of a complex array by another complex array. The first complex input is modified. | |
| static float * | discrete_laplacian (float *data_out, float *data_in, size_t nx, size_t ny) |
| Compute the discrete Laplacian of a 2D array, differences with "outside of the array" are 0. | |
| static float * | poisson_complex_filter (float *data_out, size_t nx, size_t ny) |
| Computation of the real factor which arrizes in the FFT-based discrete Poisson solver. | |
| static float ** | periodic_component_color (float **data_in_rgb, size_t nx, size_t ny) |
| Computation of the periodic component of a color image. | |
| static fftwf_complex * | random_phase (fftwf_complex *data_out, size_t nx, size_t ny) |
| Draw an array of complex numbers on the unit disc having a random phase. | |
| static float ** | phase_randomization (float **data_in_rgb, fftwf_complex *rp, size_t nx, size_t ny) |
| Phase randomization of an RGB 2D float array. | |
| static float * | compute_transition (float *transition, size_t nxin, size_t nyin, float alpha) |
| Compute the transition function used to smooth the inner boundary of the extended spot. | |
| static float ** | spot_extension_color (float **data_out_rgb, float **data_in_rgb, size_t nxout, size_t nyout, size_t nxin, size_t nyin, float alpha) |
| Extension of a color spot into a larger "equivalent spot". | |
| float ** | rpn_color_different_size (float **data_out_rgb, float **data_in_rgb, size_t nxout, size_t nyout, size_t nxin, size_t nyin, float alpha) |
| Random Phase Noise computation when the sizes of the input and the output are different. | |
| static fftwf_complex * | random_phase_with_poisson_complex_filter (fftwf_complex *data_out, size_t nx, size_t ny) |
| Draw an array of complex numbers on the unit disc having a random phase, and multiply it by the Poisson complex filter. | |
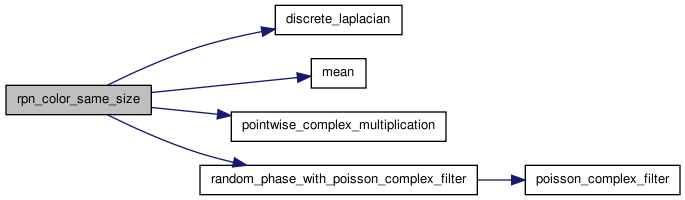
| float ** | rpn_color_same_size (float **data_in_rgb, size_t nx, size_t ny) |
| Fast Random Phase Noise when the sizes of the input and the output are the same. | |
Detailed Description
Source code for random phase noise texture synthesis. The front end functions for texture synthesis are rpn_color_different_size and rpn_color_same_size.
- Version:
- 1.2
Definition in file random_phase_noise_lib.c.
Define Documentation
| #define M_PI 3.14159265358979323846 |
macro definition for Pi
Definition at line 36 of file random_phase_noise_lib.c.
Function Documentation
| static float* compute_transition | ( | float * | transition, | |
| size_t | nxin, | |||
| size_t | nyin, | |||
| float | alpha | |||
| ) | [static] |
Compute the transition function used to smooth the inner boundary of the extended spot.
Compute the transition function used to smooth the inner boundary of the extended spot. This transition function is the convolution between a characteristic function and the standard separable molifier. More precisely the molifier is the product of an x and y function of the form:
![\[ \varphi(t) = \exp\left(\frac{-1}{1-t^2}\right) \]](../../form_7.png)
if 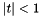 and 0 otherwise.
and 0 otherwise.
The resulting function equals 0 on the boundary and 1 on the centered inner frame of size (1-2alpha)*nxin x (1-2alpha)*nyin. It is illustrated below:
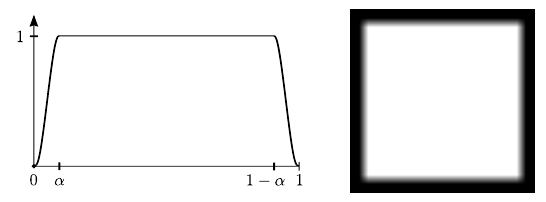
Cross section and gray-level
representation of the smooth transition function"
- Parameters:
-
transition an already allocated array of size nxin x nyin nxin,nyin input size alpha parameter in [0, 0.5) for the smoothing function (ratio for the width of the smoothing zone)
- Returns:
- transition, or NULL if an error occured
Definition at line 603 of file random_phase_noise_lib.c.

| static float* discrete_laplacian | ( | float * | data_out, | |
| float * | data_in, | |||
| size_t | nx, | |||
| size_t | ny | |||
| ) | [static] |
Compute the discrete Laplacian of a 2D array, differences with "outside of the array" are 0.
This function computes the discrete laplacian, ie 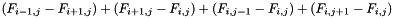 . On the border, differences with "outside of the array" are 0.
. On the border, differences with "outside of the array" are 0.
This is a slightly modified version of a function written by Nicolas Limare <nicolas.limare@cmla.ens-cachan.fr> .
- Parameters:
-
data_out output array data_in input array nx,ny array size
- Returns:
- data_out, or NULL if an error occured
Definition at line 170 of file random_phase_noise_lib.c.

| static float mean | ( | float * | data_in, | |
| size_t | N | |||
| ) | [static] |
Compute the mean of a 2D array of float type.
- Parameters:
-
data_in input array N size of the array
- Returns:
- mean of data_in
Definition at line 56 of file random_phase_noise_lib.c.
| static float** periodic_component_color | ( | float ** | data_in_rgb, | |
| size_t | nx, | |||
| size_t | ny | |||
| ) | [static] |
Computation of the periodic component of a color image.
This function computes Lionel Moisan's periodic component of an RGB color image in solving a Poisson equation with forward and backward FFT for the three channels.
Reference: L. Moisan, "Periodic plus Smooth Image Decomposition", preprint MAP5, Université Paris Descartes, 2009, available at <http://www.math-info.univ-paris5.fr/~moisan/p+s/>.
For each color channel:
- a discrete Laplacian is computed;
- the discrete Laplacian is transformed by forward DFT;
- the obtained DFT is modified by
and![\[ \hat{u}(i, j) = \hat{F}(i, j) / (4 - 2 \cos(\frac{2 i \pi}{n_x}) - 2 \cos(\frac{2 j \pi}{n_y})), \]](../../form_5.png)
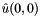 is set to be the sum of the input channel;
is set to be the sum of the input channel; - this data is transformed by backward DFT.
Below is an illustration of a color image and its periodic component.

Input image (left) and its periodic
component (right)"
- Parameters:
-
data_in_rgb input rgb float array. This input is lost. nx,ny array size
- Returns:
- data_in_rgb or NULL if an error occured
- Warning:
- The input data_in_rgb is replaced by its periodic component, and therefore is lost.
Definition at line 332 of file random_phase_noise_lib.c.

| static float** phase_randomization | ( | float ** | data_in_rgb, | |
| fftwf_complex * | rp, | |||
| size_t | nx, | |||
| size_t | ny | |||
| ) | [static] |
Phase randomization of an RGB 2D float array.
A random phase is added to the phase of each color channel.
- Parameters:
-
data_in_rgb input float array rp input complex random phase nx,ny array size
- Returns:
- data_in_rgb or NULL if there is a problem
- Warning:
- The input data_in_rgb is lost
Definition at line 518 of file random_phase_noise_lib.c.


| static fftwf_complex* pointwise_complex_multiplication | ( | fftwf_complex * | comp_in1, | |
| fftwf_complex * | comp_in2, | |||
| size_t | N | |||
| ) | [static] |
Pointwise multiplication of a complex array by another complex array. The first complex input is modified.
- Parameters:
-
comp_in1 input complex array comp_in2 input complex array N common size of both arrays
- Returns:
- comp_in1 the multiplied complex array, or NULL if an error occured
- Warning:
- The first complex array is modified !
Definition at line 121 of file random_phase_noise_lib.c.

| static fftwf_complex* pointwise_complexfloat_multiplication | ( | fftwf_complex * | comp_in, | |
| float * | float_in, | |||
| size_t | N | |||
| ) | [static] |
Pointwise multiplication of a complex array by a float array. The complex input is modified.
- Parameters:
-
comp_in input complex array float_in input float array N common size of both arrays
- Returns:
- comp_in the multiplied complex array, or NULL if an error occured
- Warning:
- The complex array is modified !
Definition at line 88 of file random_phase_noise_lib.c.

| static float* poisson_complex_filter | ( | float * | data_out, | |
| size_t | nx, | |||
| size_t | ny | |||
| ) | [static] |
Computation of the real factor which arrizes in the FFT-based discrete Poisson solver.
We have :
![\[ out(\xi_1,\xi_2) = \frac{1}{N}\frac{1}{2\cos\left( \frac{2 \xi_1 \pi}{M} \right) + 2\cos\left( \frac{2 \xi_2 \pi}{N} \right) - 4} \]](../../form_1.png)
if 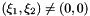 and
and 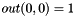 . Each coefficient is the inverse of an eigenvalue of the periodic Laplacian.
. Each coefficient is the inverse of an eigenvalue of the periodic Laplacian.
The factor 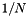 is added to normalize the Fourier transform before the inversion (note that FFTW does NOT normalize the transforms).
is added to normalize the Fourier transform before the inversion (note that FFTW does NOT normalize the transforms).
- Parameters:
-
data_out output float array nx,ny input size
- Returns:
- data_out, or NULL if an error occured
- Warning:
- The ouput array data_out has size (nx/2+1)*ny to be compatible with the R2C FFT (which takes advantage of the symmetry of the DFT of real data).
Definition at line 242 of file random_phase_noise_lib.c.

| static fftwf_complex* random_phase | ( | fftwf_complex * | data_out, | |
| size_t | nx, | |||
| size_t | ny | |||
| ) | [static] |
Draw an array of complex numbers on the unit disc having a random phase.
Draw a complex array having a random phase, that is a uniform white noise on the unit disc which is constained to be odd. The complex 2D array is only defined on the half 2D plane for compatibility with FFTW r2c and c2r transforms. This unit arrays are divided by 1/(nx*ny) for FFT normalization.
- Parameters:
-
data_out output random phase nx,ny,: size of the corresponding image
- Returns:
- the random phase data_out or NULL if there is a problem
Definition at line 433 of file random_phase_noise_lib.c.

| static fftwf_complex* random_phase_with_poisson_complex_filter | ( | fftwf_complex * | data_out, | |
| size_t | nx, | |||
| size_t | ny | |||
| ) | [static] |
Draw an array of complex numbers on the unit disc having a random phase, and multiply it by the Poisson complex filter.
Values are divided by 1/(nx*ny) for FFT normalization.
- Parameters:
-
data_out complex output having random phase nx,ny,: size of the corresponding image
- Returns:
- data_out or NULL if there is a problem
Definition at line 904 of file random_phase_noise_lib.c.


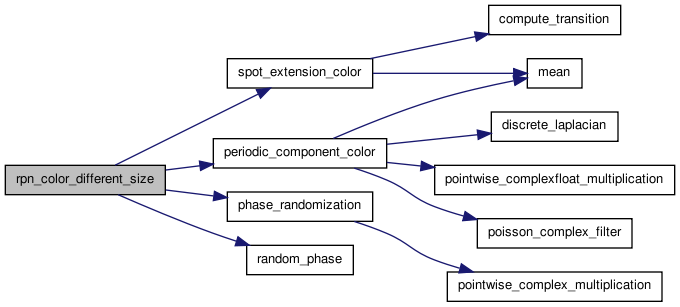
| float** rpn_color_different_size | ( | float ** | data_out_rgb, | |
| float ** | data_in_rgb, | |||
| size_t | nxout, | |||
| size_t | nyout, | |||
| size_t | nxin, | |||
| size_t | nyin, | |||
| float | alpha | |||
| ) |
Random Phase Noise computation when the sizes of the input and the output are different.
The algorithm consists of the following three steps:
- Compute the periodic component of the input image (see the function periodic_component_color) .
- Extend the periodic component in a larger equivalent spot (see the function spot_extension_color).
- Randomize the phase of the extended spot (see the function phase_randomization).
Below is an illustration of the result:

Random Phase Noise with size
extension: original image (left) and output RPN texture (right)"
- Parameters:
-
data_out_rgb output rgb float array data_in_rgb input rgb float array nxout,nyout output size nxin,nyin input size alpha parameter for the spot extension
- Returns:
- data_out_rgb or NULL if an error occured
Definition at line 850 of file random_phase_noise_lib.c.

| float** rpn_color_same_size | ( | float ** | data_in_rgb, | |
| size_t | nx, | |||
| size_t | ny | |||
| ) |
Fast Random Phase Noise when the sizes of the input and the output are the same.
When the sizes of the input and the output are the same, the computation of the perdiodic component and the phase randomization can be done simultaneously in the Fourier domain. As a consequence, the algorithm makes only two calls to the FFT algorithms (instead of four for the function rpn_color_different_size).
Here is an illustration of this function :

Random Phase Noise: input image
(left) and output RPN texture (right)"
- Parameters:
-
data_in_rgb input rgb float array. The input is replaced by the RPN output. nx,ny array size
- Returns:
- data_in_rgb or NULL if an error occured
Definition at line 1013 of file random_phase_noise_lib.c.

| static float** spot_extension_color | ( | float ** | data_out_rgb, | |
| float ** | data_in_rgb, | |||
| size_t | nxout, | |||
| size_t | nyout, | |||
| size_t | nxin, | |||
| size_t | nyin, | |||
| float | alpha | |||
| ) | [static] |
Extension of a color spot into a larger "equivalent spot".
Extend a color spot in pasting an original variance-normalized copy of the original spot and in smoothing it arround the inner frame.

Spot extension technique: the
original spot (left) is extended into a larger equivalent spot (right) by copying its periodic component in the center, normalizing its variance, and smoothing the transition at the border of the inner frame" The smoothing is done using a smooth transition function (see the function compute_transition).
- Parameters:
-
data_out_rgb output rgb float array data_in_rgb input rgb float array nxout,nyout output size nxin,nyin input size alpha parameter in [0,0.5] for the smoothing function (ratio for the width of the smoothing zone)
- Returns:
- data_out_rgb or NULL if an error occured
Definition at line 729 of file random_phase_noise_lib.c.

 1.7.1
1.7.1